Predictability is comforting. We like our daily routines, we wear the same jersey or sit in the same seat when our team plays, and we tend to remain loyal to the brands we like and trust. Unforseen events can shake our confidence in corporations, so companies spend a great deal of time preparing for the unexpected to ensure they consistently deliver on their brand promises. However, businesses today face a unique challenge in that most of their value is intangible, which must be protected and advanced in different ways.
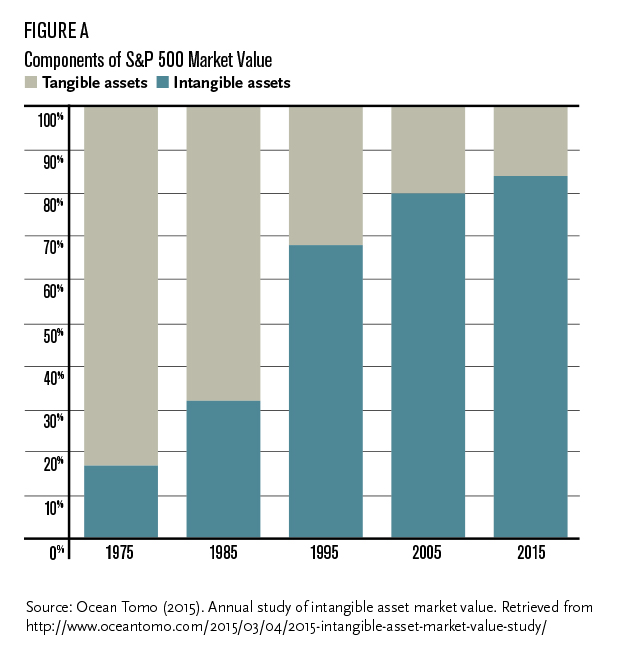
In the 1970s, a company’s market value was comprised of 83 percent tangible assets, things like the physical property, products, and machinery that the company owned. Only 17 percent of the market value of a company was made up of intangible assets, like intellectual property, human capital or reputation.[i]
Fast forward to the present day and the proportion has completely inverted. Only 16 percent of a company’s value is comprised of tangible assets, while 84 percent is made up of intangible assets (see Figure A).
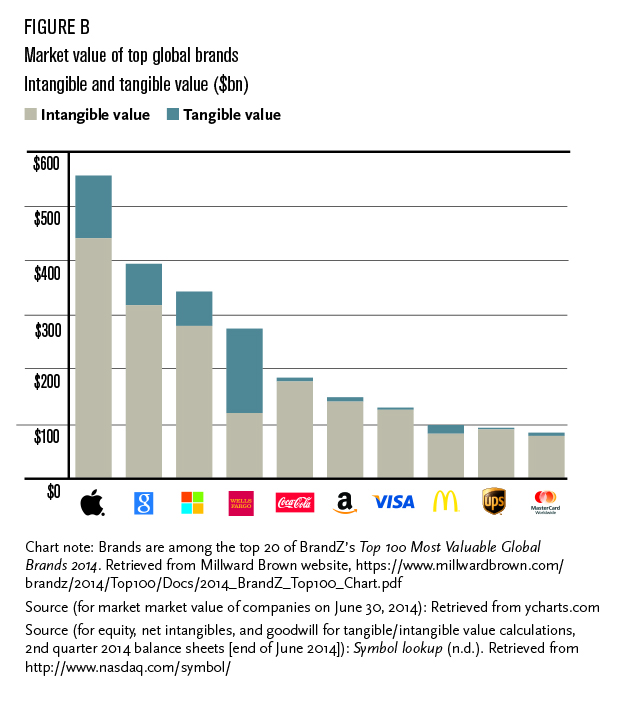
Today’s top brands are highly recognizable companies with value that is nearly entirely made up of intangible assets. They rely on their reputation, brand, intellectual property, and human capital for nearly all of their market valuation (see Figure B).[ii]
Corporate citizenship efforts can strengthen your brand. A 2016 study finds that companies with strong corporate citizenship have stronger, more resilient reputations, and consumers are less likely to assume the worst if the firm does have a misstep.[iii] Additional research finds that corporate citizenship leads to improved reputations, which in turn leads to superior market performance.[iv] CSR also contributes value to the bottom line and creates new opportunities for the business. Research has found that corporate citizenship leads to greater levels of insurance-like protection on both stock and bond prices.[v] In these ways and others, strong corporate citizenship performance can help people feel that they can predict the company’s future behavior, which in turn creates loyalty and trust.
Since both a company’s brand and its reputation are intangible, they can also feel daunting to manage. However, simple steps can help to strengthen both the brand and reputation of your company using the critical environmental, social, and governance work you do every day. Members can watch this webinar, aired November 8, 2017, to hear how member companies have made the most of corporate citizenship efforts to support their corporate brand, and how their work contributes to building and protecting the company's reputation.
Speakers:
- Brian Christiansen, Nike Global Community Impact, Nike Foundation
- Jennifer Silberman, VP, Corporate Responsibility, Target
View all resources on the Value of Corporate Citizenship on the topic page:

[i] Ocean Tomo (2015). Annual study of intangible asset market value. Retrieved from http://www.oceantomo.com/2015/03/04/2015-intangible-asset-market-value-study/
[ii] Boston College Center for Corporate Citizenship State of Corporate Citizenship 2014
[iii] Sirsly, C. A. T., & Lvina, E. (2016). From Doing Good to Looking Even Better The Dynamics of CSR and Reputation. Business & Society, 0007650315627996.
[iv] Raithel, S., & Schwaiger, M. (2015). The effects of corporate reputation perceptions of the general public on shareholder value. Strategic Management Journal, 36(6), 945-956.
[v] Shiu, Y. M., & Yang, S. L. (2016). Does engagement in corporate social responsibility provide strategic insurance‐like effects?. Strategic Management Journal.